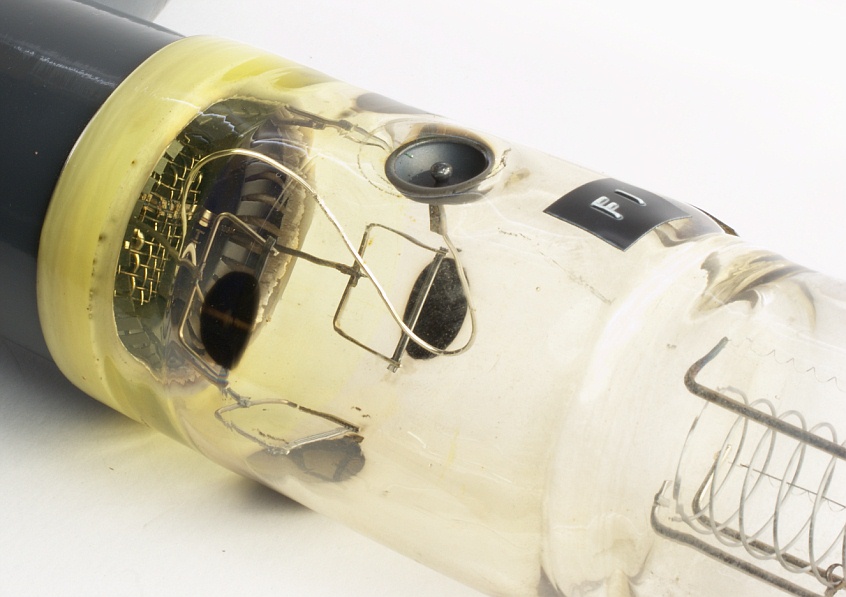
Allis-Chalmers Betatron Tube X2-82G MACHLETT
Doughnut-shaped acceleration chamber
Chambre annulaire de l'accélérateur
Ringförmige Beschleunigungsröhre
The first successful type of betatron, invented by Doctor D. W. Kerst at the University of Illinois
in 1940, is an induction electron accelerator which means that electrons are accelerated by magnetic induction instead
of by direct application of high potential.
The betatron is essentially a transformer with a torus-shaped vacuum tube as its secondary coil.
An alternating current in the primary coils holds the electrons in a stable circular orbit within an evacuated annular
chamber called a “doughnut,” and the increasing field produces a force on the electrons which accelerates them to
high velocities.
The “doughnut” is made of a porcelain which is capable of having glass sealed to it and is vacuum tight.
The inside of the bulb is coated with a thin conducting layer by industrial silvering. This coating is necessary to prevent
stray charges from building up potentials on the walls. Contact is made to the silver coating, which is then grounded
outside of the tube.
The X-rays produced by the betatron may be used in industrial and medical applications.
Documents & Links:
• D. W. Kerst The Betatron
• D. W. Kerst Development of the Betatron and its Place in Science
• Jack T. Wilson The Use of the 20 MeV Betatron in Industrial Radiography
• A similar 24 MeV tube was used at the Catholic University of Louvain (KUL, Belgium) circa 1960.
See also • Voir aussi • Siehe auch :
SVETLANA RBK6-6E Betatron 6 MeV
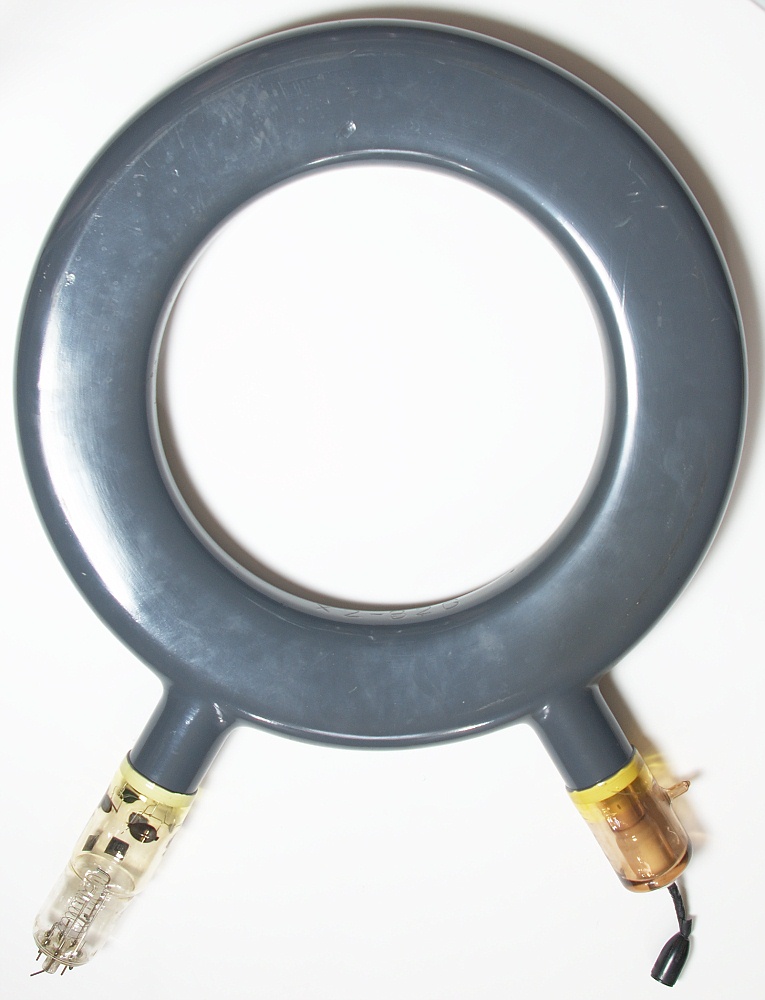

Diamètre • Diameter • Durchmesser : 48 cm • 18" 7/8
Épaisseur • Thickness • Stärke : 55 mm • 2" 3/16
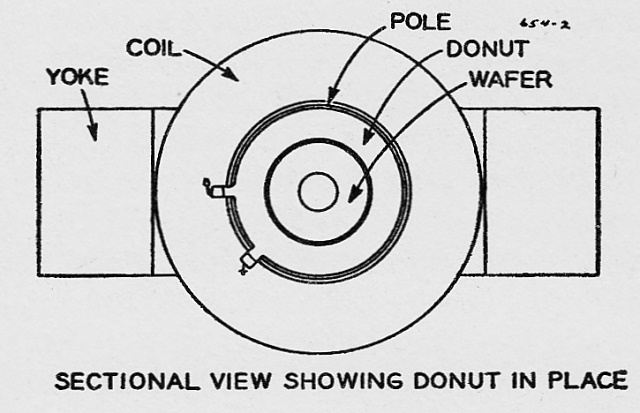
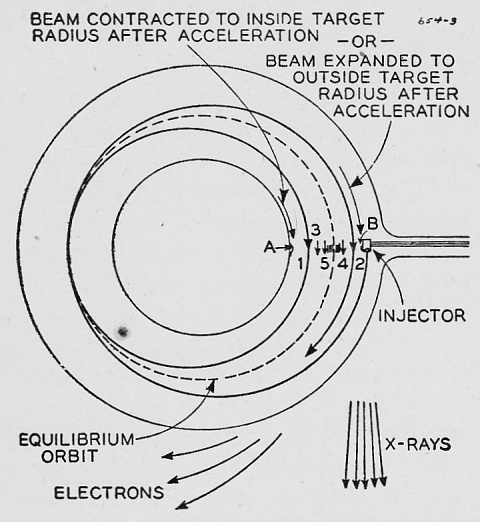
Sectional view of doughnut showing positions of injector and targets as well as electron paths

Cross section of the doughnut-shaped accelaration chamber.
The equilibrium orbit is at r0.
T is the tungsten target, A is the injector, B is a top view of the injector.
A ribbon beam of the electron from the filament F is shot out through slots in the positive plates.
P, G are negative focusing electrodes.
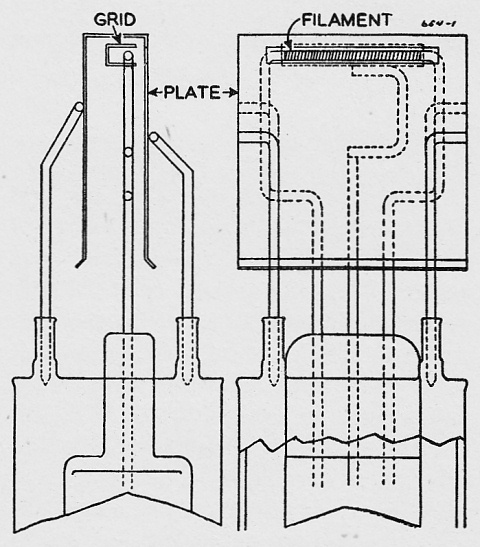
The injector
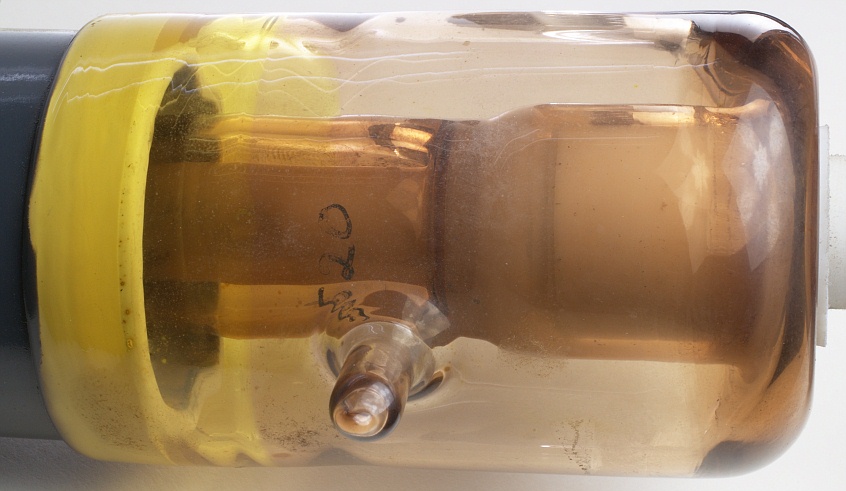



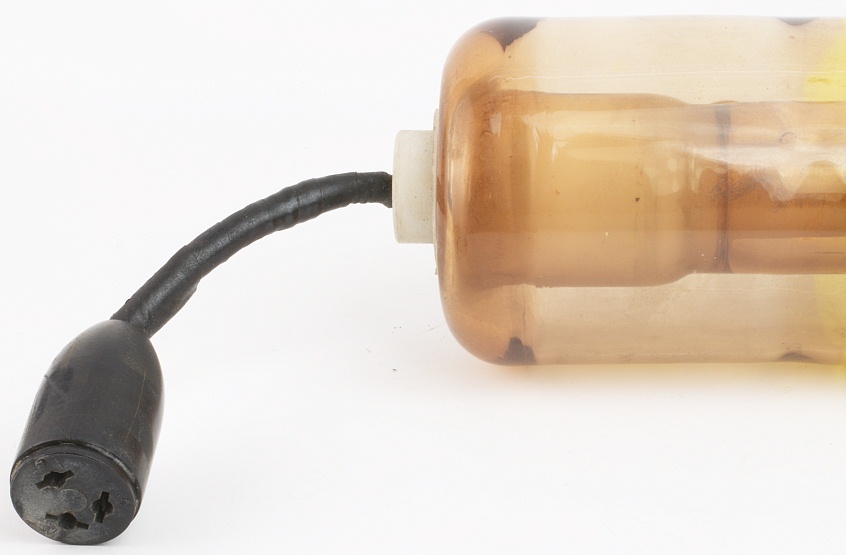

Getter and ionisation gauge
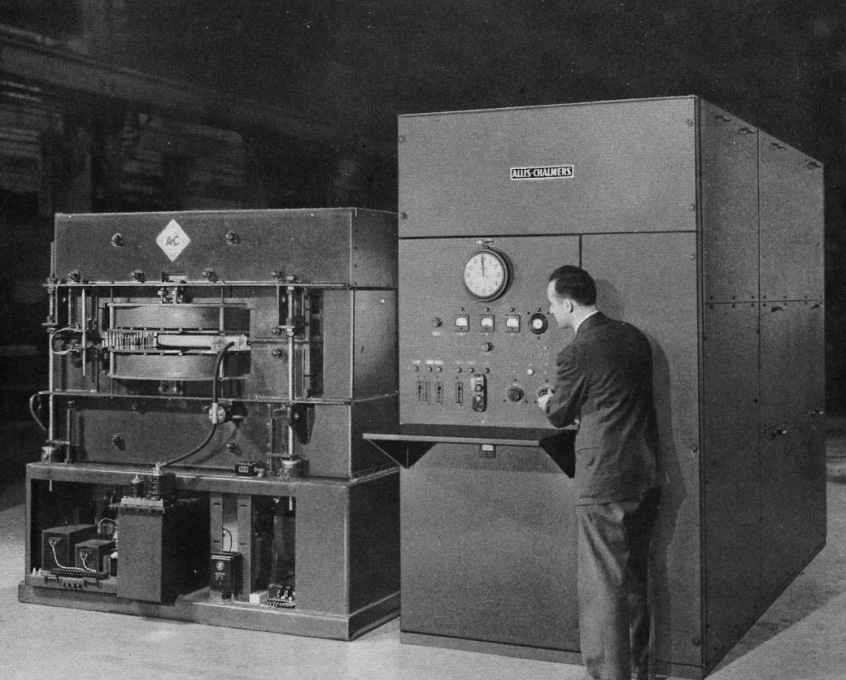
20 MeV Betatron and control equipment
Le contenu de ce site est sous copyleft  The content of this site is under copyleft
The content of this site is under copyleft  Der Inhalt dieser Website steht unter Copyleft
Der Inhalt dieser Website steht unter Copyleft
